Clik here to view.

Testing of electrical installations //
This is the simple list of basic terms you can often hear when testing and measurements of electrical installation (in general) is being performed. While expirienced electrical engineers will find this list short, I hope beginners will catch the essence and continue exploring this field of electrical engineering.
Feel free to suggest me an expression (along with description) you think it should be listed, it will be my pleasure to add it to the list and to move away from number 13 Image may be NSFW.
Clik here to view.
Ok, so here is the list:
- Active accessible conductive part
- Passive accessible conductive part
- Electric shock
- Earthing electrode
- Nominal voltage
- Fault voltage
- Contact voltage
- Limit Contact voltage
- Nominal load current
- Nominal installation current
- Fault current
- Leakage current
- Short-circuit current
1. Active accessible conductive part
Active accessible conductive part is the conductive part of an electrical installation or appliance such as the housing, part of a housing etc. which can be touched by a human body. Such an accessible part is free of mains voltage except under fault conditions.
Clik here to view.
2. Passive accessible conductive part
Passive accessible conductive part is an accessible conductive part, which is not a part of an electrical installation or appliance, like:
- Heating system pipes,
- Water pipes,
- Metal parts of air condition system,
- Metal parts of building framework
- etc.
Clik here to view.

3. Electric shock
Electric shock is the pathophysic effect of an electric current flowing through a human or animal body. Very dangerous, have eyes on your back while testing.
It’s very important to know what to do if electric shock occurs.
Clik here to view.

4. Earthing electrode
Earthing electrode is a conductive part, or a group of conductive parts, which are placed into earth and thus assure a good and permanent contact with ground.
Clik here to view.

Clik here to view.

5. Nominal voltage
Nominal voltage (Un) is the voltage which electrical installations or components of electrical installations, such as appliances, loads etc. are rated at. Some installation characteristics also refer to nominal voltage (e.g. power).
6. Fault voltage
Fault voltage (Uf) is the voltage that appears between the active accessible conductive parts and the passive ones or ideal ground in the case of a fault on appliances connected to the mains installation (connected appliance).
The figure below represents the Fault voltage (Uf) and division of the voltage into the Contact voltage (Uc) and voltage drop on floor/shoes resistance (Us).
Clik here to view.

Where:
- ZB – Impedance of human body
- RS – Floor and shoes resistance
- RE – Earth Resistance of active accessible conductive parts
- If – Fault current
- Uc – Contact voltage
- Us – Voltage drop on floor/shoes resistance
- Uf – Fault voltage
(floor material is placed to ideal ground)
7. Contact voltage
Contact voltage (Uc) is the voltage to which a human body is exposed when touching an active accessible conductive part. The body is standing on the floor or is in contact with passive accessible conductive part.
Measuring: Contact voltage is measured between the earthing electrode and two measurement electrodes connected together and placed 1m away from tested earthing electrode.
Clik here to view.
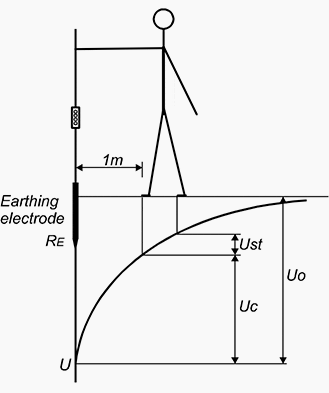
Where:
- Uo – Ground potential
- Uc – Contact voltage
- Ust – Step voltage
- RE – Earth resistance
8. Limit Contact voltage
Limit Contact voltage (UL) is the maximum Contact voltage which may be continuously present under certain external conditions e.g. presence of water.
9. Nominal load current
Nominal load current (In) is the current that flows through the load under normal operating conditions and at nominal mains voltage.
Clik here to view.

10. Nominal installation current
Nominal installation current (In) is the current that the installation draws under normal operating conditions.
11. Fault current
Fault current (If) is the current that flows to active accessible conductive parts and then to ground in case of a fault on a mains appliance.
Clik here to view.
12. Leakage current
Leakage current (IL) is the current that usually flows through isolation materials or capacitive elements to ground in normal conditions.
13. Short-circuit current
Short-circuit current (Isc) is the current that flows in a short circuit between two points of different potential.
Clik here to view.

Reference // Guide To Measurements On Electrical Installations in Theory and Practice (Download guide)